Published: December 8, 2025 | Last Updated: January 19, 2026
How AI Threat Detection Is Transforming Cybersecurity

Table of Contents
It’s becoming increasingly difficult for humans to keep up with constantly changing cybersecurity threats. Bad actors are now using advanced technologies to conduct sophisticated data breaches, zero-day attacks, and fully autonomous cyber espionage campaigns. Without proactive, real-time response capabilities that can adapt to emerging threats, businesses open themselves up to critical vulnerabilities. AI threat detection is a technology that can transform how IT and security leaders handle cybersecurity in their organizations. We’ll cover what AI threat detection is, how it is powered, what you can use it for, and challenges you might encounter.
What Is AI Threat Detection?
AI threat detection leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI and ML), including techniques like deep learning, to surface, analyze, and respond to cybersecurity threats. AI systems examine massive datasets, including system logs, user behavior, and network traffic, to pinpoint any activity that deviates from the norm.
This real-time response is especially helpful for quickly identifying zero-day threats and behaviors that may otherwise go unnoticed by human cybersecurity experts. With AI threat detection, organizations can augment their existing security team with tools that can process at scale and adapt over time to new information. AI threat detection differs from signature-based threat detection because of its continuous learning capability. Traditional security tools use predefined rules to root out behaviors and threats that are already known, while AI-based threat detection can continuously shift to respond to new threats.
How AI Threat Detection Works
A few key methodologies, including deep learning, reinforcement learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, contribute to AI threat detection processes.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning (DL) is a type of machine learning that relies on deep neural networks (DNNs), which take multi-layered approaches to analyze raw data and use it to identify complex patterns and features. This technology can detect zero-day attacks that target unknown vulnerabilities, or even identify polymorphic malware that self-modifies its code and signature to evade traditional security measures.
Deep learning algorithms can also find subtle signs of malicious activity in different sources that may not be recognized by human analysts. This includes subtle detection of linguistic or tonal changes in advanced phishing campaigns.
Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Reinforcement learning (RL) creates an agent that can respond to feedback in a trial and error process to learn how to make optimal decisions regarding threat responses over time. For example, the agent can observe an environment and take an action, like isolating a host. It will then receive a reward, taking the form of a positive numeric value, for the right action or a negative penalty for the wrong action to guide future decisions.
RL agents can also learn how to allocate real-time resources and can take on characteristics of would-be attackers to test network defenses.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) allows computers to interpret and generate human language. It’s particularly useful for analyzing data from chats, web pages, emails, and so on. It can help spot grammatical errors, anomalous questions, and unusual sending patterns to intercept suspicious activity like phishing attempts.
NLP can also take raw text and transform it into something more structured and actionable, helping AI algorithms quickly classify malicious content.
Computer Vision
Computer vision can be used to simulate seeing visual data, such as videos and images, and further interpret what’s being shown. These tools can identify fake logos and images that don’t make sense, including those created with generative AI. They can also detect slightly-off color schemes and altered layouts from cybercriminal messages and websites.
CV models can also identify odd structures in malware files after they are converted to visual patterns. This technology is also used for biometric authentication, including facial recognition, to prevent unauthorized access to areas where sensitive data is stored.
How Is AI Used in Threat Detection?
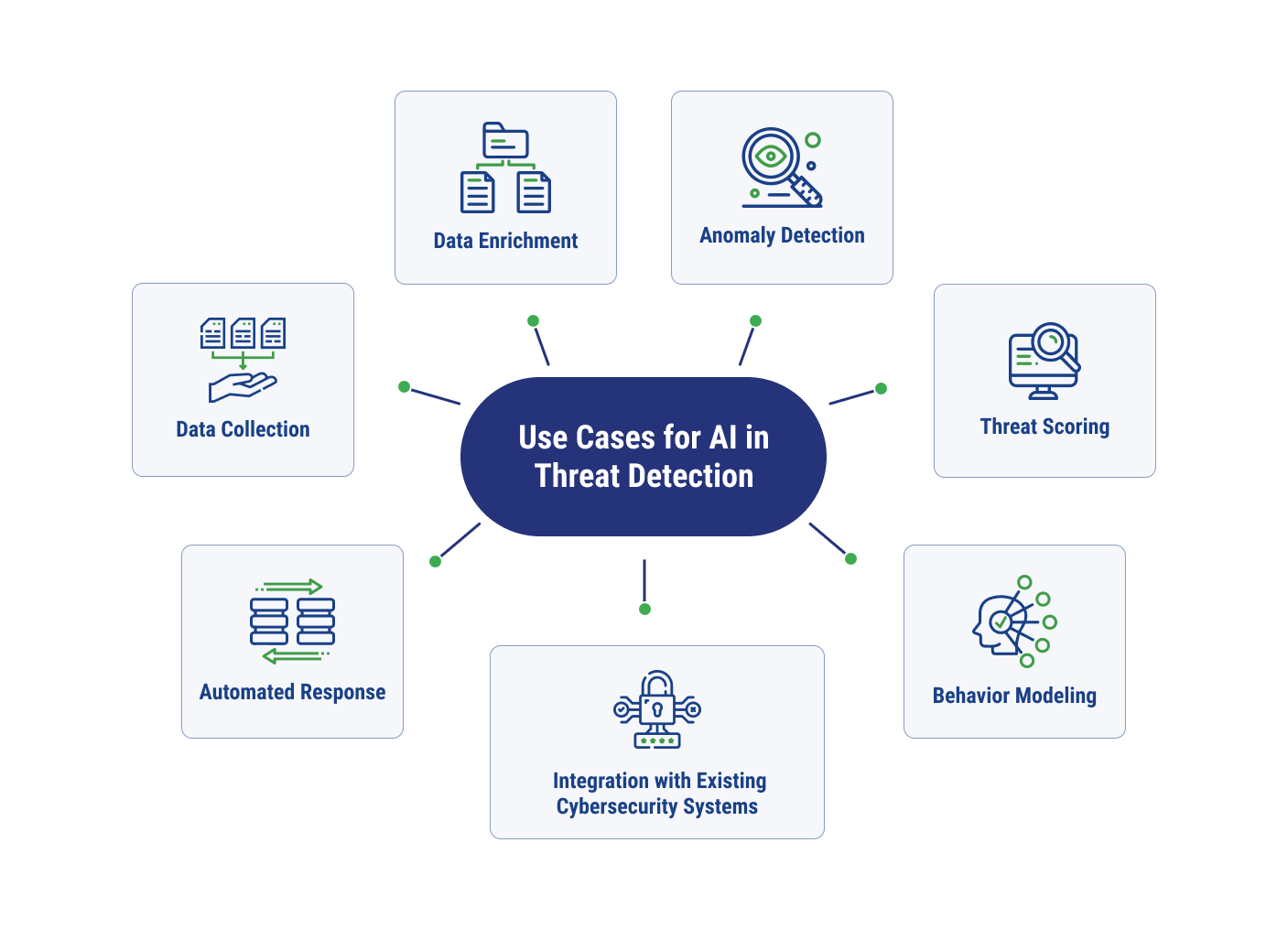
AI methodologies can be used in threat detection to collect, enrich, and identify anomalies in data. They can also be used to score the degree of the threat, mount an automated response, and create models of typical behavior to identify emerging threats. AI technology can also work in conjunction with your existing cybersecurity systems, seamlessly strengthening your defenses.
Data Collection
One significant advantage of using AI for threat detection is the vast volumes of data it can take in and process. AI-powered systems can monitor network logs, endpoints, cloud workloads, and other data sources 24/7/365, handling ingestion, normalization, and structuring of the data as it comes in.
Data Enrichment
Once it’s collected, data needs to be transformed to become more meaningful. The enrichment process includes correlation of data with external cyber threat intelligence feeds. AI-driven systems can add context in the enrichment process as well, tagging data with known threats from feeds, strange IPs, and more, which can help improve response times and detection quality.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is a key area in which AI-powered threat detection reigns supreme to traditional security methods. AI security models can identify what normal behavior is and create a dynamic baseline, which can flex as novel threats emerge. When behavior deviates from this norm, the AI tools can flag activity as anomalies. These real-time decisions are powered by inference, allowing the model to apply its training instantly to new events and flag abnormal behavior as it occurs.
Threat Scoring
From there, AI tools can prioritize threats and place higher risk scores on more severe anomalies. The higher threats can mean that the anomalies may lead to more dire consequences or may impact more sensitive data. They are also often indicative of how confident the AI model is that the behavior poses a significant threat.
AI threat detection can triage events and bring high-impact threats to the forefront, allowing human experts in a Security Operations Center (SOC) to focus on what’s critical.
Automated Response
Many threats require expert-led responses, but AI can help security teams initiate their rapid response. Automated responses can include isolation, quarantining files, or blocking suspicious IP addresses, which can stop fast-moving threats before humans have time to intervene. The human teams can then shift focus to deeply investigate more complex threats and strategize how to handle recovery efforts for non-repetitive, less time-sensitive threats.
Behavior Modeling
Each user may engage in slightly different behaviors, and that’s where behavior modeling becomes extremely valuable. This tactic involves building individual user profiles to track more subtle indications of malicious activity, such as a slow drip of strange file downloads. These actions may be missed through human observation but can be picked up more easily with pattern recognition available with AI threat detection tools.
Integration with Existing Cybersecurity Systems
AI doesn’t need to completely replace a technology stack. Instead, it can be used in conjunction with other tools to enhance the stack and deliver AI-driven insights. For example, existing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), firewall, and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools can all benefit from the integration of AI.
Key Applications of AI in Threat Detection
Machine learning and AI can provide added security for networks, endpoints, and even the physical environment for an organization. These technologies can also improve fraud detection for vulnerable industries, including retail businesses.
Network Security
The network perimeter and traffic within a network can both be protected with AI threat detection. AI-powered intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) use anomaly detection to spot previously unknown attacks. They can analyze data patterns to reduce the likelihood of false positives and generate automated responses.
Endpoint Security
Endpoints, such as desktops and mobile devices, can also be protected with AI-driven endpoint detection and response (EDR). AI tools can analyze behavior to detect attacks that may bypass traditional antivirus tools.
Managed detection and response (MDR) services often leverage advanced EDR tools, as well as broader extended detection and response (XDR) tools, to equip businesses with intelligent security automations. These AI capabilities, paired with the round-the-clock coverage from security experts that comes with MDR, can eliminate blind spots across IT environments.
Physical Security
AI-driven threat detection can also support physical environments. AI can analyze real-time video feeds to track people on surveillance systems and identify strange behaviors, such as loitering and tailgating, in which unauthorized people follow those who are authorized into a protected area. These solutions can also work with access controls to flag unusual biometric access attempts that fall outside of usual learned patterns.
Fraud Detection
Organizations can deter financial crimes by using AI systems that can analyze patterns in transactions and other digital behavior. For example, if a customer usually purchases within a certain geographical area and has an average order value range, AI can flag transactions that fall outside these norms and prevent approval in real time.
What Are the Benefits of AI in Threat Detection?
Using AI in conjunction with threat detection can speed up the analysis and response times, reduce the amount of alert fatigue IT teams have to endure, cut down on human errors, and enable greater scaling for processing data. Businesses can improve their predictive capabilities and proactively find hidden issues that allow for greater protection against emerging threats.
Speed and Efficiency
AI systems can process and respond to data in real time, making instant decisions that may take humans hours or days to complete, if they catch the threat at all.
Less Alert Fatigue
AI solutions can take instant actions before humans are alerted, reducing the number of threats to respond to. They can also prioritize the urgent, cutting down on alert fatigue.
Reduced Human Error
As AI models learn, they adapt, continuously increasing precision of the tools. This reduces risks associated with false positives or negatives, and also reduces the likelihood of human error by having an automated tool intercept possible threats first.
Scalability
The sheer volume of data that AI can process can far exceed what a human team can handle, and that level of data only seems to be growing over time. AI threat detection is scalable and can grow with complex hybrid and multicloud environments.
Enhanced Predictive Capabilities
Because these tools learn over time, they develop predictive capabilities, proactively finding vulnerabilities and hidden spots where emerging threats can reside.
How Does AI Pose New Challenges for Threat Detection?
While AI can bring new innovation and benefits to your systems, it can also introduce new risks and complexities.
Data Privacy and Compliance Concerns
Because AI systems require vast amounts of data to operate effectively and establish baselines, organizations can increase risks associated with privacy. Compromised or misused data can lead to both data privacy and compliance concerns, which can cause damage to a business’ reputation and result in legal ramifications.
IT teams can mitigate these risks by employing strict governance practices, including data encryption at rest and in transit, anonymizing personally identifiable information (PII), and implementing role-based access control to ensure that only necessary parties can access and interact with certain datasets.
False Positives and False Negatives
Without well-trained models, organizations can experience a large number of false positives or false negatives, leading to alert fatigue or missed opportunities to intervene. False positives can lead team members to take alerts less seriously, which may allow real threats to fall through the cracks. False negatives can miss novel attacks and potential vulnerabilities if the pattern recognition is not attuned well enough.
Human experts are necessary to mitigate these challenges, because they can provide real-time feedback to the models to improve their efficacy over time. Fine-tuning is necessary, especially in the early stages of AI implementation, but human intervention may become less critical as the models learn from previous inputs.
Adversarial Attacks
Attackers can manipulate AI through adversarial attacks, evading detection or compromising the integrity of established models. This can happen in the form of:
- Evasion attacks: Slightly changing malicious activities or files to bypass trained detection models.
- Poisoning attacks: Injecting malicious code into the training set to make it easier for systems to ignore threats.
- Model extraction: Reverse engineering models through repeat queries to understand how to craft future evasions.
The best way to combat these attacks is by using adversarial training, allowing models to be exposed to manipulated data so it can be better identified in real-life situations. Organizations can also use ensemble models that can cross-validate results instead of relying on just one trained model.
AI Complexity
Many AI models operate as a “black box,” and oftentimes, even developers cannot fully explain why a model made the decision it did. To integrate AI properly, including ensuring that data sets that are used are high-quality and fine-tuned, requires skilled human oversight that can be hard to come by.
Explainable AI (XAI) techniques can make models more transparent, and MDR services can augment current teams with expert human intervention from a 24/7/365 available cybersecurity team.
Strengthen Your Cyber Defenses by Combining AI and Human Expertise
When it comes to responding to cyber threats, you don’t have to look at AI and human expertise as “either/or.” Incorporate both for a unified, sophisticated response against cybercrime.
With the TierPoint Adapt Platform, you can gain the power of AI threat detection while gaining human expertise to augment your existing team. Built with MDR capabilities, the Adapt Platform includes a suite of automated solutions, alongside an always-on SOC that helps you offload critical cybersecurity tasks, so your team can focus on other priorities. Learn more about the services we offer that allow your business to thrive.

FAQ’s
Yes, AI can use real-time and historical data to detect anomalous activity and potential threats, as well as automate responses to contain and recover from the threat.
AI detection systems can identify threats such as zero-day exploits and polymorphic (changing) malware that can evade traditional cybersecurity systems. These tools can also identify advanced ransomware or phishing attacks and other threats that consist of complex behaviors by finding subtle anomalies in activity.
The predictive capabilities and ability to use behavioral analysis to find previously unknown threats make AI threat detection more advanced and more effective at improving the security posture of an organization. These methods go far beyond identifying solely preexisting threat signatures.
Table of Contents
-
Cybersecurity
Jan 22, 2026 | by Ed Mahoney
Managed Threat Hunting Explained: Benefits & Key Components
VIEW MORE -
Cybersecurity
Jan 21, 2026 | by Ed Mahoney
IPS vs. IDS in Cybersecurity: Creating a Layered Defense
VIEW MORE -
Cybersecurity
Jan 12, 2026 | by Ed Mahoney
What Is Cyber Threat Hunting?
VIEW MORE
