
Table of Contents
Cloud computing enables global access to data, but this very benefit introduces challenges around data sovereignty and cross-border compliance. Businesses that store, process, collect, and exchange data across regions or countries must be well-informed on issues of data residency, data sovereignty, and the responsibilities associated with these concepts.
What Is Data Sovereignty?
Data sovereignty focuses on the principle that a geographic region where data is collected, processed, or stored is also the region where the data is governed. Nations and regions have authority over the data that exists within their borders, which means they can make decisions about access, privacy, and security measures for this data. This is important for individuals regarding how their data will be protected, and it’s important for businesses to understand how to handle data to ensure it is compliant with varying geographical regulations. From the 30,000-foot view, data sovereignty works to protect national security and allow businesses to ensure compliance when operating internationally.
Data Sovereignty vs. Data Residency
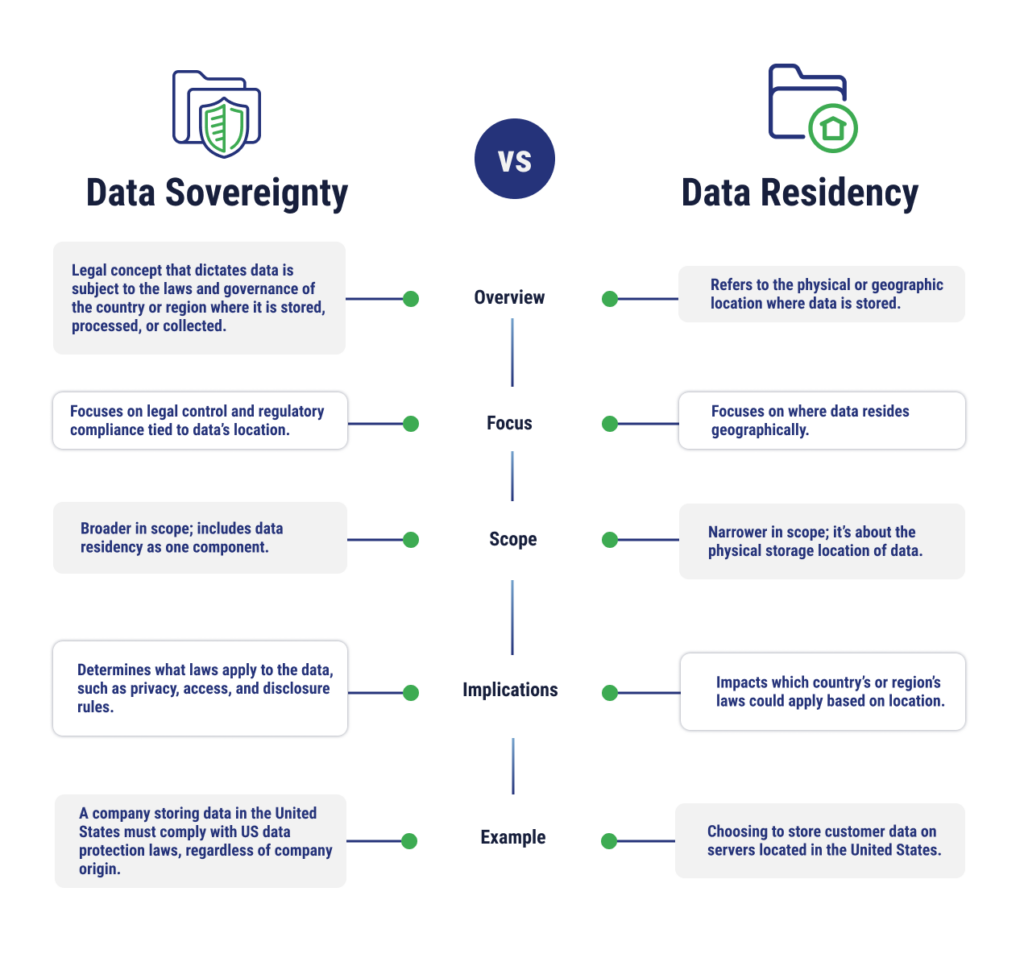
While data sovereignty may sound similar to data residency, there are differences between the concepts. Data sovereignty is a legal term that details how data must abide by a country or region’s regulations if it is stored, processed, or collected there. Data residency is a component of data sovereignty – it defines where data is stored, which in turn determines the legal jurisdiction and applicable regulations.
What Does Data Sovereignty Mean in Cloud Computing?
In cloud computing, data sovereignty has implications for how organizations must store and process their data in ways that are compliant with relevant regulations. For workloads that are in the cloud, it’s important to understand where the data centers are located and how providers manage international data transfers.
Advantages of Data Sovereignty Practices
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying compliant with data sovereignty requirements means that organizations are abiding by local or national laws, which allows them to avoid legal troubles, including penalties, fees, and sanctions.
- Enhanced Data Security and Privacy: When businesses understand their data residency, and by extension, their data sovereignty requirements, they can better control security and privacy measures, reducing risks associated with data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Greater Customer Trust: When businesses communicate their commitment to data sovereignty, customers can feel more confident about how their data is being handled.
- Business Continuity: Compliance with data sovereignty can improve accessibility even in changing political or economic conditions.
- Performance Optimization: By making changes to where data is housed and locating data centers closer to users, businesses can reduce latency and improve application performance.
Challenges to Consider with Data Sovereignty
- Compliance Complexity and Cost: Regulations around data sovereignty can morph and change over time, requiring specialized expertise and resources for businesses to remain compliant.
- Regional or Global Data Restrictions: Data localization may be required by some countries, which can prevent organizations from transferring data across borders, preventing global operations from moving forward.
- Potential Latency and Performance Issues: Businesses with operations across the globe may need to store data in multiple locations, which can negatively impact performance and latency if it is not addressed properly.
6 Tips for Ensuring Data Sovereignty in a Cloud Environment
Cloud environments can improve convenience, but they can also make data sovereignty more challenging. To ensure data sovereignty in the cloud, businesses should consider the following tips.
- Implement Strong Data Encryption Practices: With data encryption, businesses can ensure data is protected at rest and in transit, safeguarding it from unauthorized access in any jurisdiction.
- Enforce Data Access and Identity Management Controls: Employ strict access controls such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access. This can limit who has access to sensitive data. Controls should be regularly reviewed to confirm they are relevant for each type of user.
- Prioritize Local and Regional Compliance Best Practices: Your cloud strategy should include approaches that prioritize data sovereignty regulations of each region where the business operates. This can consist of in-depth research and regular review of current standards.
- Adopt a Multicloud or Hybrid Cloud Strategy: Multicloud computing distributes data across multiple cloud providers. This strategy can allow organizations to store sensitive data in regions that have friendlier, more favorable data sovereignty laws.
- Choose a Cloud Provider with Sovereign Cloud Solutions: Depending on the cloud provider your business works with, some vendors can offer solutions that cover any data sovereignty concerns. For example, TierPoint offers Azure Local which delivers Microsoft Azure services that meet data sovereignty requirements. Businesses can also utilize private cloud options for greater control depending on their needs. A private cloud, with dedicated infrastructure hosted on-premises or regionally by a provider, ensures data locality and allows for tailored security. By evaluating public sovereign clouds alongside private and hybrid or multicloud models, businesses can select the best approach to meet their specific data sovereignty, security, and operational requirements.
- Establish Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans: Data backup and disaster recovery plans improve business resilience and data availability, keeping key processes moving forward even during disruptions. Data backups also need to be stored in a way that is compliant with data sovereignty regulations.
Protect Your Company’s Data
Cloud computing, particularly hybrid and multicloud solutions, can allow businesses to be more nimble, adapting quickly to resource requirements and remaining competitive with other industry organizations. However, it also adds complexity from a data sovereignty perspective. By understanding your data, including where it is collected, stored, and processed, you can use the known data landscape to pinpoint potential data sovereignty vulnerabilities, taking the necessary steps to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
TierPoint’s Hybrid Cloud Consulting services help businesses build compliant strategies that don’t compromise on performance and security. Solutions like Azure Local make it possible to extend Azure into on-premises data centers, third-party providers, edge locations, or remote offices—offering a truly hybrid approach to data sovereignty. By partnering with an expert, businesses can address their challenges, ensure ongoing data protection, and maintain operational agility.

Table of Contents
-
Cloud
Mar 4, 2026 | by Kerri Padgett
Digital Infrastructure Trends to Watch in 2026
VIEW MORE -
Cloud
Feb 27, 2026 | by Mikael Grondahl
5 Data Management Trends to Watch in 2026
VIEW MORE -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Feb 11, 2026 | by Mikael Grondahl
Top Trends for AI in Data Management in 2026
VIEW MORE
