Published: April 30, 2025 | Last Updated: December 11, 2025
What Is AI Security? Key Concepts and Practices

Table of Contents
As organizations continue to embrace advanced technologies, we will see changing requirements for protecting digital systems. Threats will also continue to evolve, increasing the burden for IT teams to strive to protect their infrastructure in an ever-shifting environment. Robust artificial intelligence (AI) models and solutions can boost an organization’s security posture, but these technologies can also introduce new risks. We’ll cover what AI security is, common use cases in different industries, and how to protect against AI security threats.
Introduction to AI Security
AI security refers to the technique of leveraging AI solutions as part of an organization’s cybersecurity posture. This approach goes above and beyond human analysis and traditional rule-based systems to develop stronger, more intricate pattern recognition systems, deeper levels of insights, and more automated tasks, saving organizations time, money, and exposure to human error.
AI security methods work well in conjunction with human intervention, triaging the most urgent tasks and allowing for more time for human analysis on critical issues.
Key Components of AI Security
There are three key components to AI security: Data privacy and protection, system integrity and reliability, and threat detection and prevention.
Data Privacy and Protection
To maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data, IT teams may take a multilayered approach, implementing AI solutions that contain some or all of the following:
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Creating access control mechanisms
- Anonymizing data
- Validating, monitoring, and managing data
- Adding checks for data corruption
- Implementing storage and backup solutions
System Integrity and Reliability
AI applications can be used to improve system integrity and functionality, ensuring that IT systems will function without being compromised or experiencing unexpected failures. This can include automated failover from a production site to a backup site in the event of a natural disaster, automatically allocating resources to meet current demands, or completing routine maintenance tasks to prevent larger system breakdowns. Additionally, AI can be used to perform continuous monitoring for environmental anomalies, such as temperature spikes, water leaks, or smoke, to reduce risk and avoid costly damage.
Threat Detection and Prevention
Rule-based security solutions can cover a wide range of threats, but AI-powered solutions go deeper by analyzing large sets of security data and learning to spot anomalies that may not have been covered in previous rulesets. When trained properly, these tools can forecast potential attack vectors and change defensive responses accordingly.
AI Security Use Cases Across Industries
How businesses implement AI security measures will depend on the types of models they use, where they are hosted, and what their most common vulnerabilities will be. The following use cases are common across industries.
- Fraud Detection: While especially important in finance, insurance, healthcare, and e-commerce industries, fraud detection can uncover anomalies and pinpoint fraudulent activities quickly. These can include slight changes in behavior that might be missed by human observation.
- Advanced Threat Detection: AI technologies can analyze system logs, endpoint activity, and network traffic to identify zero-day exploits, data breaches, and advanced persistent threats, allowing businesses to respond more quickly and limit damage from malicious activity.
- Cybersecurity Automation: Instead of conducting all manual processes, many cybersecurity tasks can be automated, including vulnerability scans, incident response steps, and threat intelligence analysis. Automated processes can help IT teams prioritize their time and focus on the most severe threats, and the automatic tasks can reduce the likelihood of human error.
- Identity and Access Control (IAM): Most people in a business do not require access to every part of a system. Identity and access management (IAM) allocates access based on a person’s role and job functions, preventing them from accessing unnecessary resources. This limits the risk from compromised accounts.
- Phishing Attack Prevention: Emails can be a major source of vulnerability for a business without any protective measures or training. Phishing attacks try to trick users into providing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. AI-powered systems can block phishing messages using natural language processing and machine learning techniques to find unusual writing patterns or altered email addresses.
- Endpoint Protection: Some threats that haven’t yet been discovered may be able to move past antivirus software, and this is where endpoint protection comes into play. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can use AI to detect unusual behavior at endpoints, and can automate responses to isolate affected devices to prevent the spread of a breach.
- Cloud Security: Any organization with cloud infrastructure can implement AI solutions to improve security in these environments. AI tools can analyze activity in the cloud to find potential threats, automate security assessments, conduct real-time monitoring, and enact established security policies.
- Vulnerability Management: If organizations are not quick to update systems based on known vulnerabilities, cybercriminals can use them as a way to gain access. Keeping track of new vulnerabilities can be time-consuming, but AI tools can lessen the manual burden by running automatic scans, patching software, and performing real-time attack responses.
Strategies for Enhancing AI Security
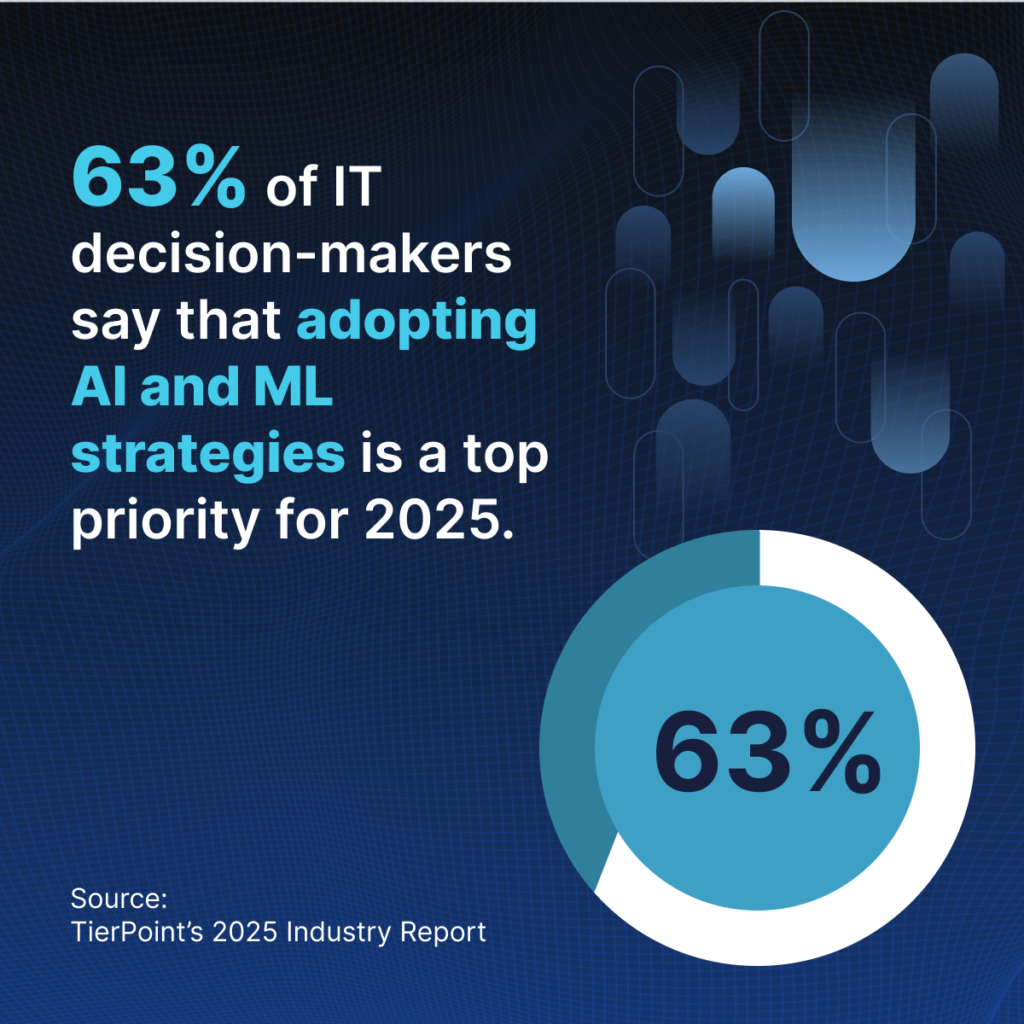
63% of leaders say adopting AI and machine learning (ML) is a top priority this year, especially when it comes to boosting security.
If your organization is looking to enhance security using AI, consider incorporating the following strategies:
- Implementing Robust Encryption Methods: With encryption, data is protected when sending to another party or device (in transit) and when stored (at rest). The right encryption method for your data will depend on how sensitive it is and where it is stored, but it’s important to have encryption at these points, as well as a tool for encryption key management. Encryption tools like AES-256 can be used for file systems and databases at rest, and TLS/SSL protocols can be used for data in transit.
- Utilizing Secure Data Storage and Access Controls: Stored data can be susceptible to data breaches and attacks from malicious insiders. Only allow access to data when absolutely necessary by implementing role-based access and the principle of least privilege. AI-based tools can also identify behavior that is outside of the norm, which may indicate someone is acting in a potentially suspicious way.
- Developing Resilient AI Models: Resilient AI models are those that are created with security considerations right at the beginning and are regularly tested throughout their lifecycle. Adversarial training and regularly validating models can help build resilience.
- Implementing Physical Security Systems: Physical access to critical infrastructure should not be overlooked. AI-powered physical security systems, including facial recognition, biometric authentication, and smart surveillance help prevent unauthorized access to data centers or secure environments. Additionally, environmental monitoring with AI can detect temperature anomalies, water leaks, or smoke early, minimizing the risk of damage and unplanned downtime.
- Conducting Regular Security Audits: The IT infrastructure, AI models, data pipeline, and all other elements of the IT environment should be part of regular security audits. AI tools can analyze security logs, monitor for compliance violations, and create reports on the current state of an organization’s security posture. The frequency of these audits will depend on how much sensitive data is being protected and what other security measures are in place.
Potential AI Security Threats and How to Address Them
While AI solutions can help protect your organization against threats, they can also introduce new attack vectors. AI models are prone to data protection vulnerabilities, adversarial attacks, and privacy breaches. IT teams using AI models must also ensure they are compliant with relevant industry regulations, and they should establish their own code of ethics for AI deployment.
Potential AI Security Threats and How to Address Them
While AI solutions can help protect your organization against threats, they can also introduce new attack vectors. AI models are prone to data protection vulnerabilities, adversarial attacks, and privacy breaches. IT teams using AI models must also ensure they are compliant with relevant industry regulations, and they should establish their own code of ethics for AI deployment.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Personal and sensitive data can be subject to various industry regulations, including PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA. Businesses that don’t abide by these guidelines can be subject to fees, sanctions, and damaged trust. Introducing AI models into the mix can make it harder to ensure systems are compliant. This is where model transparency becomes especially important, as well as data governance policies and periodic compliance assessments.
Adversarial Attacks
Adversarial attacks use malicious inputs in an attempt to hinder the performance of AI models. Similarly, data poisoning uses malicious samples to try to bias or cause malfunctioning in the AI system. Anomaly detection, strong model training systems, behavior monitoring, and data validation tools can protect against these attacks.
Desirable AI models may also be targeted with model extraction or inversion techniques, where bad actors attempt to capture the intellectual property within an AI model. Obfuscating the data layer, watermarking the intellectual property, and using strict access control measures can help protect proprietary data.
Privacy Breaches
AI technologies are also susceptible to common privacy breaches and other threats, including malicious insiders. Standard cybersecurity strategies can strengthen AI systems against infrastructure attacks and data breaches. This can include system logs, activity monitoring, in-house security training, and access controls.
Ethical and Safe AI Deployment
For AI models to be effective, they should be resistant to manipulation and provide predictable, dependable outputs based on their training. This requires robust AI models that are trained against misleading or malicious inputs using techniques like adversarial training and input sanitization.
A system also maintains its integrity when AI models are easy to explain and interpret. By understanding how an AI model reaches a decision, teams can uncover potential bias, errors, or vulnerabilities in the model. Tools can be used to learn more about model behavior and audit for bias.
The hardware and software also need to be secure under the AI systems. Like other applications a business may use, this includes periodic patching, regular vulnerability management, and ensuring secure configurations are in place.
Take the Next Step in Boosting Your Security Posture
In IT modernization, AI has quickly shifted from a cutting-edge technology to a normal part of business. If you’re looking to leverage AI tools to improve security and optimize processes, but you’re not sure how to take the first step, download TierPoint’s business applications for AI/ML whitepaper for ideas.

Table of Contents
-
Cybersecurity
Dec 8, 2025 | by Ed Mahoney
How AI Threat Detection Is Transforming Cybersecurity
VIEW MORE -
Cybersecurity
Nov 26, 2025 | by Matt Pacheco
EDR vs MDR vs XDR: Key Differences Explained
VIEW MORE -
Cybersecurity
Nov 17, 2025 | by Matt Pacheco
Cloud Infrastructure Security: Key Threats & Best Practices
VIEW MORE
