
Hybrid cloud continues to be a popular approach for many businesses, with 73% of organizations leveraging a hybrid cloud strategy. When it comes to private cloud, Microsoft Azure Stack is the most popular option. 38% of organizations are currently running workloads in this private cloud environment.
Integrating Azure Stack with the public cloud can allow organizations to balance the best of both worlds – the flexibility and scalability of public cloud with on-premises resources and security controls enabled by Azure Stack. This is also a great way to leverage existing investments for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure while still retaining an on-premises environment. We’ll discuss which Azure Stack solution is best for public cloud integration, the benefits of conducting this integration, and how to architect Azure Stack solutions to integrate most effectively with public cloud.
Which Azure Stack Solution is Best for Public Cloud?
Each Azure Stack solution offers unique advantages for public cloud environments. However, Azure Stack Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) best suits businesses that are focused on public cloud integration. This is because Azure HCI comes with strong hybrid capabilities, Azure connectivity, and centralized management features.
Azure Stack Hub, while providing deep integration and advanced features, may seem like the best option for a hybrid cloud environment. However, it’s most appropriate for large-scale deployments and organizations looking to take advantage of the full potential of hybrid cloud. For businesses seeking a more flexible and cost-effective solution, Azure Stack HCI offers an easier way to integrate on-premises infrastructure with Azure’s public cloud services, making it a strong option for those beginning their hybrid cloud journey.
Key Benefits of Integrating Azure Stack with Public Cloud
Regardless of what you choose, integrating Azure Stack with the public cloud comes with several benefits, including greater workload mobility, consistent management options, improved scalability, better cost-efficiency, and optimized resource utilization.
Seamless Workload Mobility
Integrated workloads can move between Azure Stack and the public cloud with ease. This configuration allows businesses to strategically place workloads based on cost, security, and compliance concerns.
Consistent Management, Monitoring, and Operations
Tools such as Azure Arc can help businesses manage and monitor their entire hybrid environment within a unified view. The same tools and resources can be used in both Azure Stack and the public cloud to make management easier. The comprehensive view also makes the monitoring process more efficient and proactive.
Improved Flexibility and Scalability
One of the greatest benefits of hybrid cloud is that businesses can break past previous physical limitations they may have experienced in on-premises environments. Infrastructure can be scaled up or down based on resource needs. Organizations also gain the flexibility to incorporate more innovative services and technologies enabled by Azure Stack.
Enhanced Cost-Efficiency
Idle infrastructure results in unnecessary expenses. The pay-as-you-go model in the public cloud helps reduce costs by right-sizing resources based on actual usage. Integrating between Azure Stack and the public cloud means businesses can take advantage of centralized tools and processes, saving time and reducing operational overhead.
Optimized Resource Utilization
With a more flexible environment, resources can be used where it makes the most sense from a performance, cost, and security perspective. Critical tasks can be left to on-premises resources, while peak workloads can be offloaded to the public cloud. This approach also improves disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring critical data and applications are safeguarded and quickly recoverable in case of an outage.
Better Performance
By effectively optimizing resources and managing workloads, businesses can experience lower latency and an improved user experience. Processing important data on-premises removes the latency associated with sending data to the public cloud. Users then enjoy faster response times and a more seamless experience.
Architecting Azure Stack for Public Cloud Integration
Successfully integrating Azure Stack with a public cloud environment requires a comprehensive architecting plan that includes workload assessment, networking, security controls, management, budgeting, and more. Some of the most important steps are detailed below.
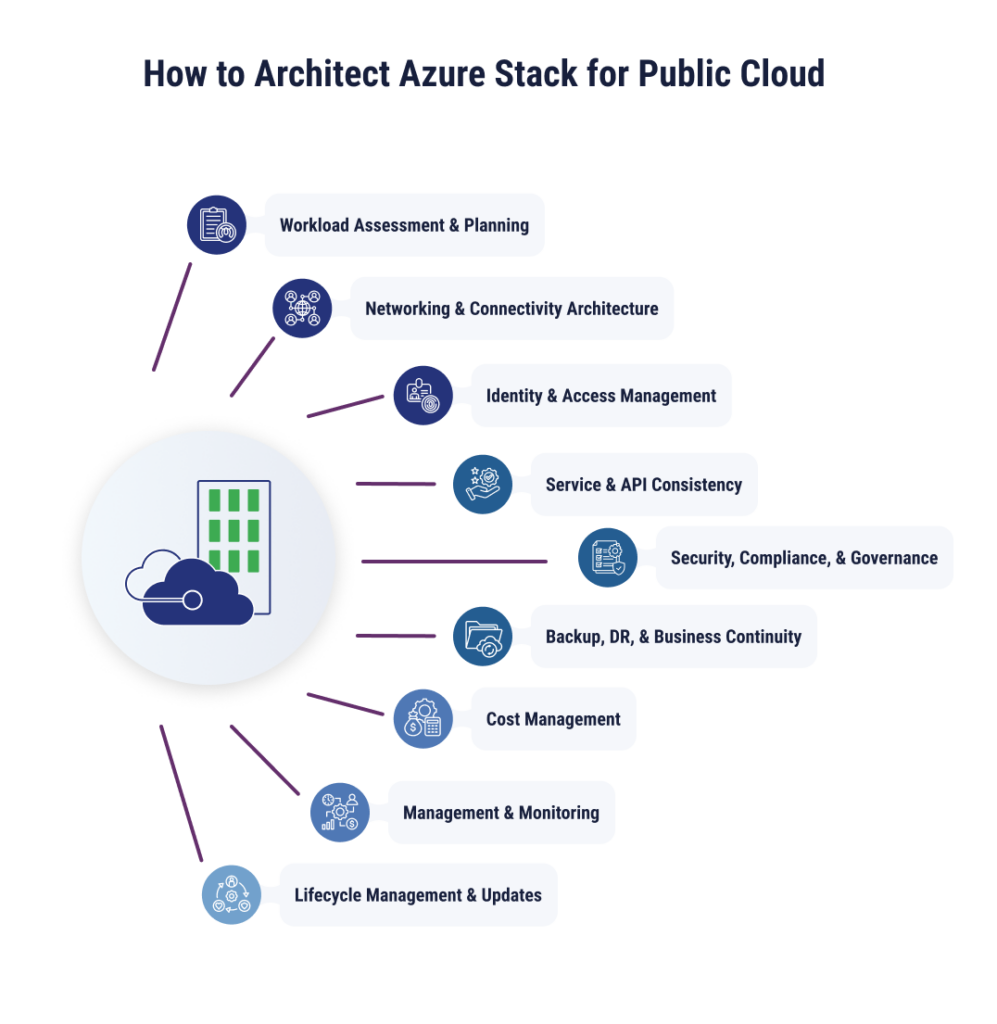
Workload Assessment and Planning
Start by understanding what you want to get out of the integration. Azure Stack bridges the gap between an on-premises environment, or third-party data center, and the public cloud. Identify the use cases in your business where Azure Stack will be the most beneficial. For example, if you have certain data sovereignty needs, moving some of these workloads to Microsoft Azure Stack can improve performance and satisfy regulatory requirements.
On the other hand, some workloads may benefit more from public cloud features, such as elasticity, on-demand scaling, and access to advanced services, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) technologies.
Networking and Connectivity Architecture
To integrate effectively, businesses need to engage in best practices for establishing connections between Azure Stack and Azure native which are:
- Secure
- Low-latency
- High-bandwidth
- Redundant
Consider incorporating tools and resources that maintain uptime and business continuity such as virtual private networks (VPN) and Azure ExpressRoute, as well as third-party cloud connectivity tools like Megaport and Zayo.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
It’s important to have consistent identity management across your hybrid environment to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Extending Microsoft Entra ID to Azure Stack can allow businesses to define role-based access control. Assigning specific roles to users means that organizations have more granular control over their users, reduced risk of unauthorized access, and simplified management around user permissions because the focus is on roles instead of individual permissions.
Microsoft Entra ID also centralizes the management of user identities, permissions, and groups, simplifying the administration process. This can also improve user experience through a single sign-on (SSO) portal.
Using Entra ID means that businesses can enact conditional access policies, such as factoring in device, location, and user risk in the authentication process.
Implementing IAM across environments enhances your organizational security, improves user management efficiency, ensures compliance with data privacy and security requirements, and provides a better user experience when accessing resources.
Service and API Consistency
Key services APIs should be available and consistent between Azure Stack and Azure native. Any potential gaps or differences should be noted and mitigated. Not all Azure services are available in Azure Stack, so businesses need to account for and plan for these gaps.
For example, both environments support load balancing. However, Azure native offers additional advanced features that can’t be found in Azure Stack. If an application your organization relies on requires load balancing, you need to confirm that the basic load-balancing features in Azure Stack meet your needs. For more advanced features, businesses may have to implement custom solutions or keep certain workloads on Azure native.
Security, Compliance, and Governance
The security framework you employ must span both Azure Stack and Azure native. Consider what you need for encryption, threat detection, and incident response. This framework should include:
- Data encryption with key management and industry-standard practices
- Threat detection with security monitoring, security analytics, and notifications from threat intelligence feeds
- Incident response plans that outline steps in the event of a security breach, including team members and preventative testing measures
Azure Policy and Compliance Manager can enforce regulatory requirements and assign policies to resources in Azure Stack and Azure native. This can help you safeguard your data, enforce regulatory requirements, and minimize the risk of potential security incidents.
Backup, DR, and Business Continuity
The right disaster recovery (DR) plan leverages Azure Stack and Azure native to ensure a seamless failover and recovery. Your business should have backups in place so that when an incident occurs, you can switch seamlessly.
While Microsoft doesn’t currently allow direct failback from Azure Site Recovery (ASR) to Azure Stack, organizations can still leverage ASR for robust disaster recovery strategies. By replicating data from on-premises environments to the public cloud using ASR, businesses can create a secondary disaster recovery site in the cloud.
Azure Backup can routinely back up Azure Stack virtual machines (VMs) to the public cloud. In the event of a disaster, backed-up VMs can be restored to Azure Stack, restoring infrastructure and applications quickly. Critical workloads can also benefit from hybrid backup, replicating data between Azure Stack and the public cloud to improve redundancy and data protection.
Cost Management
Azure has built-in tools to monitor and optimize costs across Azure Stack and Azure native, including Microsoft Cost Management. This tool can apply cost allocation tags to track spending associated with specific resources and ensure that resources are rightsized to avoid incorrect provisioning. You can also set up cost alerts to get notified about unexpected spending increases.
It’s important to understand that there are cost implications for running workloads in both environments, including capital expenditures for Azure Stack hardware and facility costs for on-premises environments. There are also operational costs for resources. Understand the full environmental expenses to create a cost-effective plan that works for your organization.
Management and Monitoring
A consistent management experience relies on tools and practices that can be used for the central management of both environments. These include Azure Arc, which manages resources from a single console, and Azure Monitor, which monitors resource health and performance in Azure Stack and Azure native.
Continuously monitoring the health of resources in your hybrid environment, configuring alerts, and automating responses to issues can help you maintain high availability.
Lifecycle Management and Updates
Lifecycle management and updates are crucial for maintaining a well-functioning hybrid environment. Regularly updating and maintaining your Azure Stack infrastructure ensures it stays in sync with Azure native, preserving feature parity and security. Azure Stack’s update mechanisms, such as Azure Stack Update Manager and Azure Stack Lifecycle Manager, streamline the process of applying updates to your on-premises environment. By staying up-to-date, you can benefit from the latest security patches, performance improvements, and new features introduced in Azure.
Unlock the Full Potential of Public Cloud
By integrating Azure Stack, businesses can unlock the full potential of the public cloud and the benefits that allow organizations to thrive in the digital age. Taking a hybrid approach can help businesses meet evolving needs while improving flexibility, scalability, and security.
Partnering with a trusted managed services provider, like TierPoint, can allow your business to unlock the potential of a hybrid environment that combines public cloud and Azure Stack. Learn more about our Managed Azure Stack services and reach out to one of our experts today.

