
Businesses that invest in moving workloads to the cloud open up their environment to new scaling, performance, and innovation opportunities, but the cloud migration process isn’t always cut and dry. Without careful planning, IT leaders can find themselves over budget, over time, and ill-equipped to deal with unexpected technical, cultural, and operational issues.
We’ll talk about the nine most common cloud migration challenges, and what you can do to address and overcome them.
Why is Cloud Migration Difficult?
Cloud migration is difficult because it affects every layer of an organization, presenting technical, organizational, and logistical challenges. Complex dependencies, differences between the existing system and the target cloud environment, and the sheer volume of data to be moved all add to the difficulty. The need to minimize downtime can further impact project timelines, as well as the feasibility of certain cloud migration strategies.
The size and intricacy of a migration also contribute to the total cost. Lack of budget or inadequate resource allocation can be major barriers to completing a cloud migration project or may lead to compromises in terms of scope or quality.
9 Cloud Migration Challenges
When your organization starts to transition to the cloud, you may encounter a few common cloud migration challenges. Understanding these major concerns before you begin, and planning how to address them, will help you streamline your project and capture the benefits of the cloud faster.
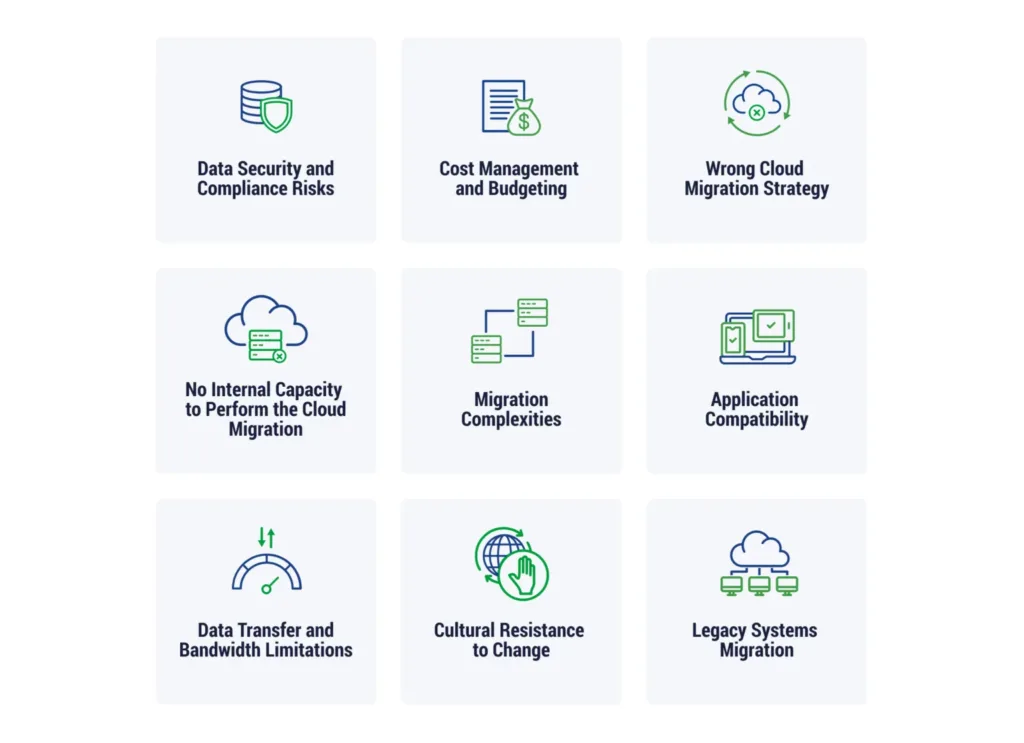
1. Data Security and Compliance Risks
A new environment with a new cloud provider can introduce fresh compliance and security risks. While major cloud providers have physical, network, and data security measures in place, they may lack some of the controls that on-premises infrastructure offers.
It’s important to know what your potential provider does and doesn’t cover during your cloud migration, including data loss prevention, especially if the data you’re moving is highly sensitive. Conducting a thorough risk assessment and understanding the shared responsibility model between your organization and the cloud provider is crucial for maintaining data security during the migration.
The same goes for compliance. Microsoft Azure, for example, has a long list of compliance offerings. However, you will need to be mindful of additional measures you need to have in place to be fully compliant in your new cloud environment. Ensure your chosen cloud provider meets requirements set by national, regional, and industry-specific laws, like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare organizations. Regulatory compliance is essential to avoid legal and financial repercussions in cloud-based environments.
2. Cost Management and Budgeting
A cloud migration is no simple feat. It requires a dedicated team, lots of planning, and many different types of resources to work well. Plus, while a data center migration alone can be expensive, businesses also need to proactively address the long-term challenge of high cloud costs, which can come from an unoptimized or unmonitored cloud environment.
Carefully planning a cloud migration is one of the best defenses against uncertain costs. Still, you can encounter unexpected challenges, such as issues with data compatibility, surprise technical problems, or the need to hire more people or invest in more tools along the way. A good plan can get you close to an accurate estimate, but it’s important to stay flexible in case of unknowns.
To decrease the risks of cost overruns and control spend, conduct a comprehensive assessment of the existing infrastructure and applications. This evaluation will help identify potential bottlenecks, compatibility issues, and areas that may require significant changes for successful migration. Additionally, collaborating with experienced cloud consultants can provide valuable insights and reduce unforeseen expenses.
Proactively implementing cloud financial management strategies during migration is also key. Cloud service providers offer various pricing models, and selecting the most cost-efficient options that align with your company’s needs is crucial. Utilize tools offered by your provider to monitor resource utilization and optimize costs continuously. For example, you can consider:
- Rightsizing instances
- Setting up automation for resource provisioning and deprovisioning
- Utilizing cloud cost models like reserved instances or spot instances that ensure consistent cost savings
3. Establishing the Right Cloud Migration Strategy
Without a clear roadmap, you can face cloud migration challenges like increased costs, prolonged timelines, and potential disruptions to your business operations. A well-planned cloud migration strategy should include:
- A detailed estimate of the costs
- A workload prioritization plan
- A realistic timeline
- The necessary human and technical resources to complete the project
Being fuzzy on any of these points can weaken an otherwise effective strategy. You also need a plan for troubleshooting and testing post-migration, so you can quickly identify and remedy problems.
It’s also important to decide between a “big bang” or phased migration. A big-bang rollout is often a less-than-ideal strategy because it involves planning to migrate all workloads at once. If something goes wrong, you can experience more downtime compared to migrating in stages. On the other hand, a phased migration offers significantly more stability while ensuring business continuity, though it may slightly extend timelines.
A poor strategy can also mean choosing the wrong provider for your needs, which is another common mistake that can lead to difficulties during the migration. Failing to assess and align to your business needs and requirements adequately could result in suboptimal performance or higher costs than necessary.
4. Skills Gaps and Training Needs
Many companies have had a hard time sourcing help to perform cloud migrations due to the growing cloud skills gap, which has remained one of the two largest IT skills shortages since 2021.
A lack of cloud expertise and skills can significantly impede a smooth and successful cloud migration. Migrations involve a complex set of tasks that require in-depth knowledge of cloud technologies, infrastructure, and migration best practices. Without the necessary expertise, organizations may struggle to make informed decisions and execute the migration efficiently.
Skilled cloud professionals can:
- Optimize resource utilization
- Quickly identify and resolve problems
- Leverage best practices for securing data and applications in the cloud
- Navigate technical intricacies, including dependencies
- Identify potential roadblocks
- Discover and implement critical success factors
If you don’t have the right people internally, engaging with cloud consultants or MSPs with proven expertise can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the migration process.
5. Data Migration Challenges
Cloud migration is difficult primarily because it’s a complex process. The type of data being moved, the size of the data, and the dependencies that need to be accounted for when moving to a new cloud provider make cloud migration a difficult puzzle to solve.
Some data is incompatible with the cloud and can cause issues if it is not reformatted or restructured prior to the migration. There can also be compatibility issues with hardware and software, or problems with network connectivity. Complexities can also arise from differences in opinion over how cloud migration should be handled.
6. Application Compatibility
Poorly optimized applications, network latency, and inefficient cloud infrastructure are all factors that can contribute to low application performance after cloud migration. Sometimes, an application that works great in an on-premises environment experiences a performance degradation in the cloud. It’s important to identify the root of the issue so performance can be boosted; otherwise, productivity or adoption of the application can lag.
7. Data Transfer and Bandwidth Limitations
Another cloud migration challenge stems from the sheer volume of data transferred from on-premises systems to the cloud environment. When dealing with vast datasets or mission-critical applications, data transfer can take a significant amount of time, leading to potential delays and increased downtime.
The data transfer process heavily relies on the available network bandwidth. If your internet connection or network infrastructure has limited capacity, it can significantly slow down the migration process. To overcome bandwidth limitations and achieve a smooth transition, organizations need to implement efficient data migration strategies. This might involve:
- Using incremental data transfers
- Prioritizing critical data
- Employing data compression techniques to optimize the use of available bandwidth
8. Change Management and Organizational Resistance
Even when everything goes right, organizations can face significant cultural resistance to change. Team members who are used to legacy systems may be resistant to moving their work processes to a cloud-based service, simply because it’s not what they’re used to doing.
To address resistance effectively, proactively manage change and communication throughout the migration process. Early involvement and engagement of end-users in the planning and decision-making stages can foster a sense of ownership and inclusion, making them more receptive to the changes. Identifying “champions” among the team members who are enthusiastic about the cloud and its potential benefits can be instrumental in encouraging others to embrace cloud migration initiatives.
A phased approach to migration can also help reduce resistance. By gradually transitioning workloads and applications to the cloud, companies can give team members time to adapt and gain confidence in the new environment.
9. Legacy Systems Migration
Legacy systems often rely on outdated technologies, programming languages, or proprietary protocols that are not inherently compatible with modern cloud platforms. Due to this, migrating legacy applications and integrating legacy systems with the cloud can be tricky.
More often than not, legacy applications require considerable modifications and adaptations to ensure smooth communication and data. They also may lack some of the native security features and encryption mechanisms found in today’s cloud platforms, and may have complex interdependencies with other applications or databases. Migrating and integrating these interconnected components to the cloud requires meticulous planning to avoid disruptions and maintain a cohesive system while keeping sensitive data secure.
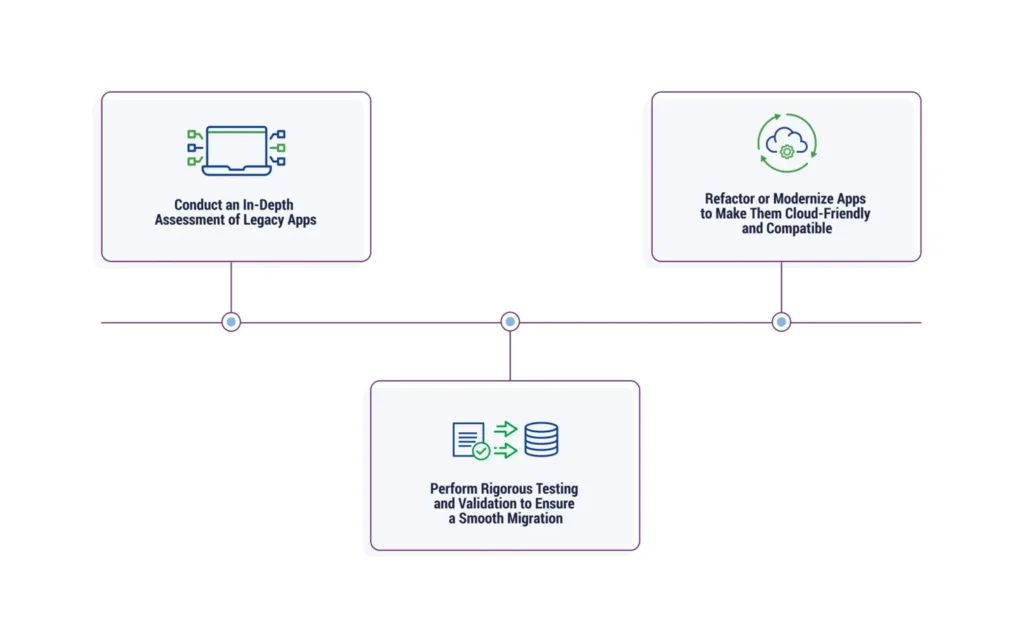
When integrating legacy systems with the cloud, it’s crucial to perform rigorous testing and validation. Additionally, during the planning phase, it’s essential to conduct an in-depth assessment of legacy applications (including their architecture, data, and dependencies) to uncover integration points and compatibility errors early. Consider refactoring or similar application modernization strategies to make them cloud-friendly and compatible with the cloud environment.
Conquer Your Cloud Migration Challenges With TierPoint
Understanding how to navigate common cloud migration challenges is just as important as preventing them. When unexpected circumstances arise, the right expertise can keep your project on budget and on time.
TierPoint has helped organizations overcome every one of these challenges, from cost control to security concerns, many times over. We develop highly agile, tailored migration roadmaps to guide your transition to public, private, or hybrid cloud, meeting your business needs with minimal downtime.
Our migration experts are ready to help you plan for now and for the future, leveraging cloud computing to accelerate your growth and innovation.

FAQs
When migrating to Azure, businesses need to be mindful of the cost of the project, the time it will take to migrate, and security differences between an on-premise environment and a cloud environment.
Moving data smoothly, ensuring security and compliance measures are met, and migrating data effectively are all key challenges in AWS cloud migration.
